The history of the High Level Bridge, Newcastle
Opened in 1849, High Level Bridge at Newcastle was part of the objective to create a continuous line from London to Edinburgh.
Designed by Robert Stephenson, the bridge was to combine rail and road traffic. It was the first in the world to do so.
High, not wide
The Newcastle & Berwick Railway secured the Act to build its line in 1845. It stipulated that the company should construct a combined road and rail bridge across the River Tyne. The bridge would be between Newcastle and Gateshead and was to be completed within four years.
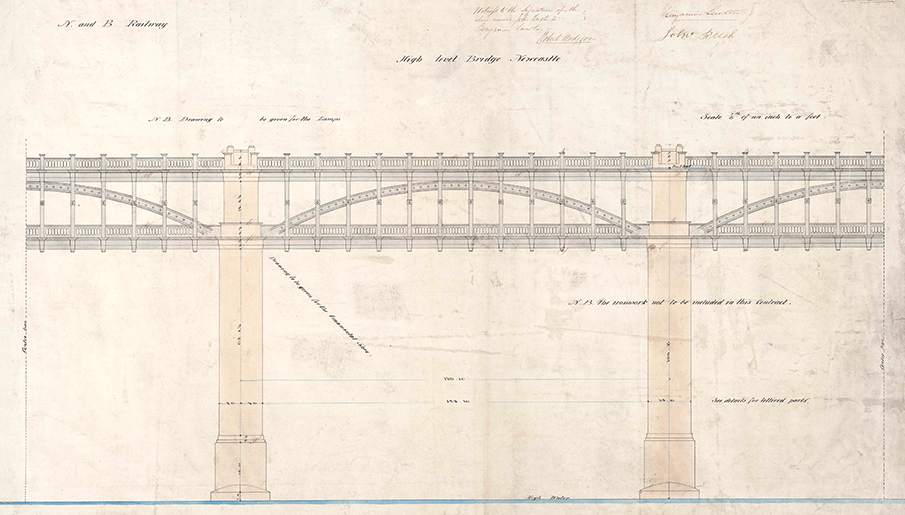
The bridge was designed by Robert Stephenson and detailed drawings were made under the supervision of Thomas E Harrison. To avoid excessive width, and thereby expense, it was decided to carry the railway above, rather than beside, the roadway. The roadway itself was designed to be 20ft (6m) wide with a 61/2ft (2m) footway on either side. The combined width allowed three standard gauge tracks to run across the top rail level of the bridge. The overall length of the bridge was to be 1338ft (408m).
Construction and use
The bridge was a tied arch (or bow-string) bridge. The main structural elements were made of either cast or wrought iron. It had in total six spans each 125ft (38m) in length. The cast iron bows supported the railway while wrought iron ties supported the road deck below. To enable a level line for the railway across the deep and wide Tyne valley, the roadway was built at 96ft (29m). And the railway 120ft (37m) above high water on the river. Contracts for the production of the ironwork were let to local firm Hawkes, Crawshay & Co of Newcastle.
The bridge sits on five masonry piers, 50ft (15m) thick and 16ft (5m) wide. The River Tyne, at the point the bridge is constructed, was no more than 3ft (1m) deep at low water. Its bed consisted of some 30ft (9m) of silt before underlying bedrock could be reached.
A recent invention, the ‘Nasmyth Steam Pile Driver’, was used for the first time in bridge building. It enabled the piles for the bridge foundations to be driven down to the bedrock quickly and efficiently. Rush & Lawton of York were contracted to build the five main masonry piers. As well as the land arches on each side carrying the approaches. 50,000 tons of stone was quarried near Newcastle, mainly at Heddon on the Wall.
To assist in the construction work a wooden viaduct was built immediately to the east of the permanent one. This temporary structure was opened to railway traffic on 29 August 1848. This was just a year before the High Level Bridge itself was opened by Queen Victoria on 28 September 1849. The public roadway over the bridge was not completed and opened until some six months later.
In 1906 King Edward VII opened the King Edward railway bridge nearby, which provided a shorter route into Newcastle station. Today the High Level Bridge is used as a turning loop on the East Coast Mainline.
Conservation awards
Between 2001 and 2008 we undertook an extensive refurbishment project of the bridge. This strengthened the structure as well as restoring some if its original features. For its research into the use of cast iron, as well as the conservation techniques it employed, the project received prestigious awards. This included the 2009 Grand Prize for Conservation from Europa Nostra.
Did you know?
The original roadway over the bridge required the manufacture of 200,000 specially shaped wooden blocks.